
Neurotrauma from Impact

Brain damage from football, improvised explosive devices, and childhood falls has spurred a surge of funding for research on impact brain damage. Damage seems to result in slow growth of tangles of Tau proteins at the damaged sites, but behavioral changes due to the damage may not appear for years. This has delayed understanding of the causes of behavioral alterations now understood to be due to impact dementia.
Animal research is necessary to find any early indicators of impact and to test therapies. One preliminary finding has been that a repeated impact before the first damaged tissue has healed and stabilized results in a much worse outcome than one impact alone. This has implications for how a concussion should be treated. The patient, although feeling fine and fully recovered, should not go back to the battlefield, or the football field, for a considerable time that needs to be defined.
Several instruments have been developed to create controlled impacts on the skull or brain, or spinal cord, of research animals. There are pneumatic, gravity and electrically driven devices. Prior to 2006, such instruments were massive, noisy, and awkward to position.
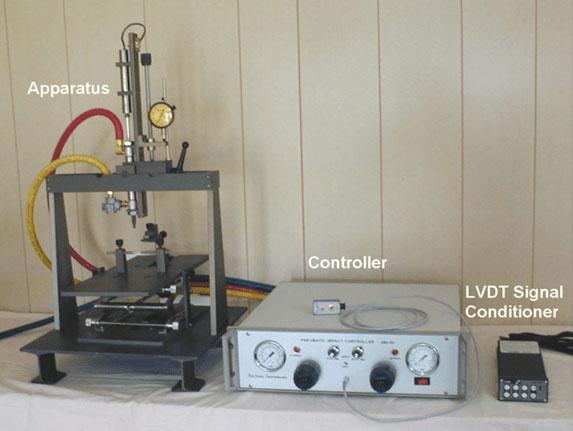
In 2006, a device came on the market with a small, lightweight impeller, and the entire actuator could be mounted on a stereotaxic instrument. Mounting on a stereotaxic instrument allows positioning the position and angle of the impact reproducibly relative to Bregma with 10 micron resolution. Depth of penetration is also set with the stereotaxic instrument, with the aid of a contact sensor. Impacts may be either open head or closed head, that is, directly on the brain, or on the skull surface. Both have been shown to generate permanent neural damage.
How do you select what instrument is best for your experiments?
The first question usually asked is “how much force does it have?” This is the wrong question, whose answer, at least with open head injury, for all of these devices, is zero, or very nearly so. Simply put, the brain does not push back. A force sensor between the brain and the Impactor tip would read very little. Further, with a slow push, the brain will compress and reposition and avoid much damage, if the entry is not too deep or extreme. So depth is not entirely the right measure. So what is the relevant variable?
Momentum might be, if the probe was going to be stopped by the target. However, these devices have preset stops that limit penetration. The moving part is stopped by a metal stop, not the target tissue. If two identical probes, but one with a ton behind it, and one with an ounce behind it, traveling at the same velocity, impact the brain, are not slowed by it, and penetrate to a depth where it is then stopped by its own stop, the result should be identical. Except stopping the ton probe will required great force, and it will probably overshoot, and then vibrate in the brain much more than the ounce probe, and make a very loud impact noise.
Further, there is always a limited distance available for acceleration, and there must be very fast acceleration to work up to a reasonable impact velocity. More mass will require greater force to be applied during acceleration, which will require more power, a more expensive controller, and more noise to stop it.
So in the end, a light impeller probe with controlled velocity and preset maximum depth of penetration should yield more reproducible results. The probe must have enough mass that it is not stopped or slowed noticeably by the brain tissue. That requirement is easy to meet if the mass is moving at high velocity.
Some contend that the duration the probe is in contact is crucial, other say not. Most instruments can control the contact duration, and that will remain until rigorous tests show duration does or does not affect the degree of damage.

About the presenter

Charles Scouten acquired his Ph.D from SUNY Binghamton in 1980 with a dissertation entitled “Location of Neurons Mediating Androgen’s effect on Copulation, Urine Marking, and Body Weight”.
El contenido de Leica Biosystems Knowledge Pathway está sujeto a las condiciones de uso del sitio web de Leica Biosystems, disponibles en: Aviso legal.. El contenido, incluidos los webinars o seminarios web, los recursos de formación y los materiales relacionados, está destinado a proporcionar información general sobre temas concretos de interés para los profesionales de la salud y no está destinado a ser, ni debe interpretarse como asesoramiento médico, normativo o jurídico. Los puntos de vista y opiniones expresados en cualquier contenido de terceros reflejan los puntos de vista y opiniones personales de los ponentes/autores y no representan ni reflejan necesariamente los puntos de vista ni opiniones de Leica Biosystems, sus empleados o sus agentes. Cualquier enlace incluido en el contenido que proporcione acceso a recursos o contenido de terceros se proporciona únicamente por comodidad.
Para el uso de cualquier producto, debe consultarse la documentación correspondiente del producto, incluidas las guías de información, los prospectos y los manuales de funcionamiento.
Copyright © 2024 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.