The BOND RX Stainer - Automated Multiplexing Solutions

Multiplex immunohistochemistry is fast becoming a useful research tool as it enables a more in-depth analysis of precious tissue samples. This is often associated with increased labor in the laboratory; however, the BOND RX stainer can automate your multiplex solutions to give you more freedom to discover.
Identifying disease biomarkers and effective therapeutic targets requires research that delves into increasingly fine molecular detail. To add to the complexity of molecular biology, we understand that all molecular events do not work in isolation. All events, whether at the gene or protein level, homeostatic or pathogenic will influence many other cell types, cascading to tissue and organ function. Tissue samples are a valuable resource to better understand these mechanisms as they hold genetic, protein and tissue biology, however, these samples can often be a limited resource.
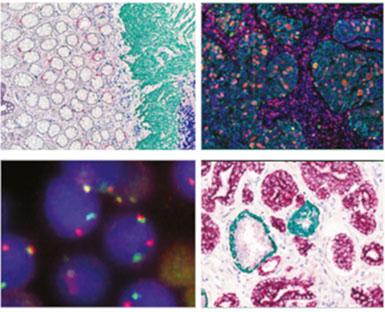
Aside from time, automated multiplexing conserve the integrity of precious and limited tissue samples to answer an overarching research question. For example, you may want to investigate the expression of novel biomarkers as well as analyzing the infiltration of specific immune cell lineages in tumor samples as part of a research project. Multiplex IHC/ISH has the potential to identify all markers of interest on one tissue section, thus maximizing the amount of biological information acquired for a more in-depth analysis and understanding.
To accompany this, the BOND RX stainer also allows you to automate your unique and customized staining protocols. If you are using locked-nucleic acid ISH, interested in circulating tumor cells or immunofluorescent multiplexing, then there is no need to modify and/or reoptimize your tests. This system enables these tests, allowing you a personalized approach to biomarker/drug discovery.
Automating multiplex IHC/ISH therefore combines more freedom with efficient use of important tissue samples that ultimately results in more opportunities to unfold the story of complex diseases.
Here are some example articles that have used the BOND RX stainer for real-life research applications for specific investigations:
CSF1R Ligands IL-34 and CSF1 Are Differentially Required for Microglia Development and Maintenance in White and Gray Matter Brain Regions.1
Investigating Radiotherapy Response in a Novel Syngeneic Model of Prostate Cancer.2
RX-5902, a novel beta-catenin modulator, potentiates the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in preclinical models of triple negative breast cancer.3
To enhance those research discoveries, below is a summary of key features of the BOND RX stainer:
- Speed: Stain 2-6 markers on 30 slides in as little as 2.5 hours, reducing time performing manual staining steps, and increasing time for innovation.
- Flexibility: 3 trays means 3 experiments run simultaneously to help answer those all-important research questions.
- Customization: Automate your own tests and tailor the BOND RX stainer to perform fully customized protocols with specific incubation times, temperatures, and every step of your multiplex staining. Yes, every step!
- IHC and ISH : Run IHC and ISH on the same sample in the same run to understand the spatial relationship between gene expression and cellular phenotype.

- Fluorescent or chromogenic: Fluorescent and chromonic detection are both possibilities on the BOND RX stainer for up to 6 markers – Take your pick!
- Open System: Use your own antibodies, probes, amplification, and detection systems with the open container system.
- Consistency: The covertile function ensures consistent reagent application with minimal, yet sufficient reagent volume. No more parafilm!
- Efficiency: Generate minimal waste and access all bulk reagents at any time (yes, even when the experiment is running). Low reagent volumes are also visibly highlighted during the run.
Want to know more? Read more here or contact us for more information.
Start innovating today!

About the presenter

Rhian is a Scientist from Swansea University in Medical and Healthcare Studies and was featured in several collaborative publications. Rhian’s research-based background focused on tissue-based pathology in Multiple Sclerosis, primarily using immunohistochemical analysis and in vitro molecular techniques. She spent a short period conducting routine PCR testing for COVID-19 at the end of 2020.
References
- Easley-Neal C, Foreman O, Sharma N, Zarrin A.A, Weimer R.M. CSF1R Ligands IL-34 and CSF1 Are Differentially Required for Microglia Development and Maintenance in White and Gray Matter Brain Regions. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:2199.
- Haughey CM, Mukherjee D, Steele RE, et al. Investigating Radiotherapy Response in a Novel Syngeneic Model of Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2020;12(10):2804.
- Tentler JJ, Lang J, Capasso A, et al. RX-5902, a novel β-catenin modulator, potentiates the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in preclinical models of triple-negative breast Cancer. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:1063.
Related Content
Leica Biosystems content is subject to the Leica Biosystems website terms of use, available at: Legal Notice. The content, including webinars, training presentations and related materials is intended to provide general information regarding particular subjects of interest to health care professionals and is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, medical, regulatory or legal advice. The views and opinions expressed in any third-party content reflect the personal views and opinions of the speaker(s)/author(s) and do not necessarily represent or reflect the views or opinions of Leica Biosystems, its employees or agents. Any links contained in the content which provides access to third party resources or content is provided for convenience only.
For the use of any product, the applicable product documentation, including information guides, inserts and operation manuals should be consulted.
Copyright © 2024 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.