H&E Image Quality & Tissue-based Research

Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) is a common laboratory technique used in research to provide a detailed view of tissue architecture. Hematoxylin is basophilic and used to visualize nuclear detail with a blue nuclear hue, and eosin is used for visualization of the cytoplasm, organelles, and extra-cellular components in a pink/red color.
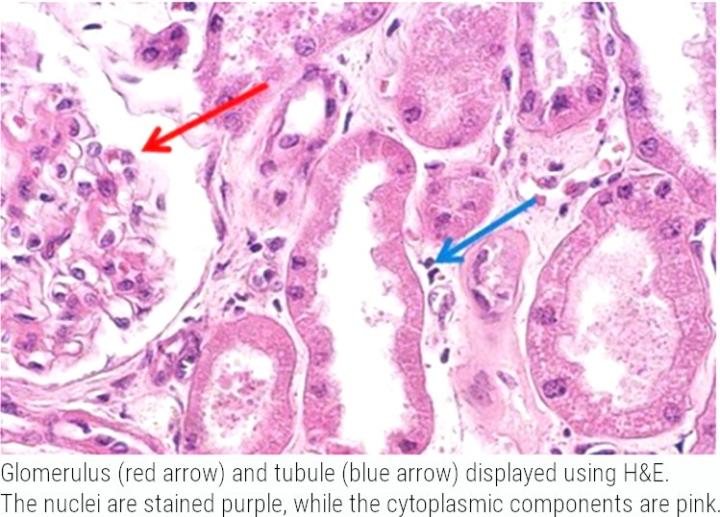
This information can be used in tissue-based research to identify the organization, and similarly disorganization of cells, nuclear abnormalities, and inflammatory infiltration that is often associated with diseases such as cancer, or as a measure of drug efficacy and/or toxicity drug development. For accurate interpretation of histological H&E slides, staining standardization and consistency is important, as is the image quality of the slides for analysis.
Digital pathology is being increasingly used by biopharmaceutical companies and contract/clinical research organizations to streamline the drug development process for discovery and pre-clinical research. Converting glass slides into digitized whole slide images opens new possibilities for remote global collaboration and for quantitative analysis.
Interpretation of H&E slides by pathologists is often semi-quantitative or qualitative and can be subject to inter-observer variation due to differences in experience. Quantitative analysis of pathological features, particularly algorithms that are automated, can help to reduce bias, standardize inter-observer interpretation, while simultaneously reducing the time spend on analysis and increasing the amount of data returned.
This opportunity may become especially relevant with the advent of assays which are difficult to discern with the human eye, such as multiplex, or quantify more complex parameters such as morphological changes, or markers which exhibit diffuse staining characteristics across multiple cellular compartments.
For example, Martino et al., (2020) used Leica Biosystems Aperio AT2 in combination with on open source image analysis software (QuPath) to scan and analyze H&E and immunohistochemically stained tissues. They used this digital analysis approach to explore the possibility of predicting Ki67 labeling (biomarker used to detect proliferation-committed fraction of neoplastic cells), using H&E stained sections of oral squamous cell carcinoma. They uncovered that nuclear hematoxylin mean optical density, reflecting chromatin condensation, was a potential parameter that could detect Ki67 positive cells, confirmed by sequential immunohistochemical staining. The ability to predict the H&E equivalent of immunohistochemical positivity has the possibility to conserve precious tissue resources and maximize the amount of data obtained from the same slide.

Figures 2 & 4 from Martino et al, (2020) showing:
-
An overlapping field with SCC (squamous cell carcinoma) obtained from the Ki67 immunostained H&E decolored sample. (A) H&E squares indicate some of the selected cells for feature analysis); (B) Ki67/MIB1
IHC
(immunohistochemical). Red and green squares, respectively, represent positive and negatively annotated cells. -
Representative image showing the graphical report of Ki67 status prediction. The overlapped squares color shows the real Ki67 status as observed in the corresponding field of Ki67 immunostained section.
Image quality during scanning is important for manual interpretation, but also in applying such algorithms to ensure that the parameters being quantified are a true representation of pathology and not an artifact.
Leica Biosystems offers a total solution for histological staining, including stainers, digital pathology scanners and slide management software.
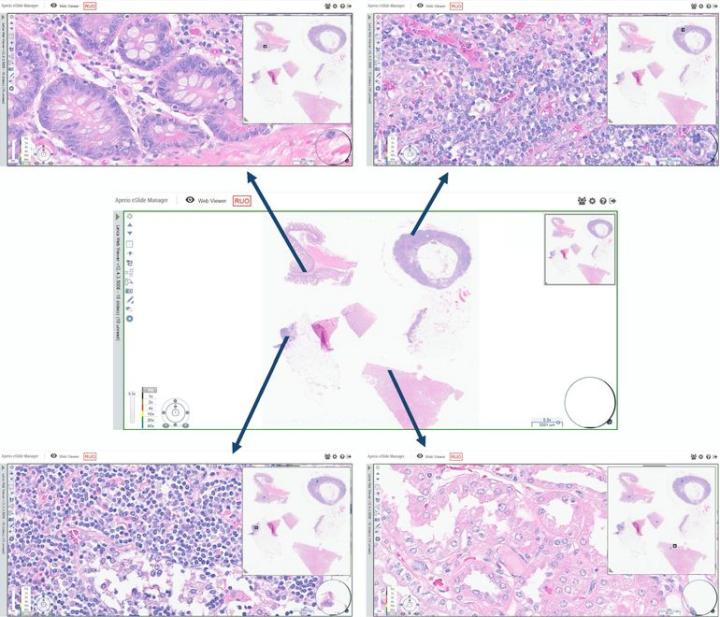
Check out the images below for some examples of H&E stained slides that were scanned with Aperio GT 450 and viewed with Aperio eSlide Manager. See for yourself the clarity and quality of the images produced.
About the presenter

Rhian is a Scientist from Swansea University in Medical and Healthcare Studies and was featured in several collaborative publications. Rhian’s research-based background focused on tissue-based pathology in Multiple Sclerosis, primarily using immunohistochemical analysis and in vitro molecular techniques. She spent a short period conducting routine PCR testing for COVID-19 at the end of 2020.
References
- Martino F, Varricchio S, Russo D, Merolla F, Ilardi G, Mascolo M, dell’Aversana GO, Califano L, Toscano G, De Pietro G, Frucci M, Brancati N, Fraggetta F, Staibano S. A Machine-learning Approach for the Assessment of the Proliferative Compartment of Solid Tumors on Hematoxylin-Eosin-Stained Sections. Cancers. 2020; 12(5):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051344
Related Content
Leica Biosystems content is subject to the Leica Biosystems website terms of use, available at: Legal Notice. The content, including webinars, training presentations and related materials is intended to provide general information regarding particular subjects of interest to health care professionals and is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, medical, regulatory or legal advice. The views and opinions expressed in any third-party content reflect the personal views and opinions of the speaker(s)/author(s) and do not necessarily represent or reflect the views or opinions of Leica Biosystems, its employees or agents. Any links contained in the content which provides access to third party resources or content is provided for convenience only.
For the use of any product, the applicable product documentation, including information guides, inserts and operation manuals should be consulted.
Copyright © 2025 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.